Beyond Flow Cytometry Capture the Real-Time Vitality of Regeneration with Our Breakthrough CD Factor Detection Technology
The revolutionary Low Speed Centrifugation Concept (LSCC) has proven that the key to superior tissue regeneration lies in the selective enrichment of leukocytes and platelets. As research confirms, lower RCF protocols significantly boost the release of essential growth factors like VEGF and TGF-β1.
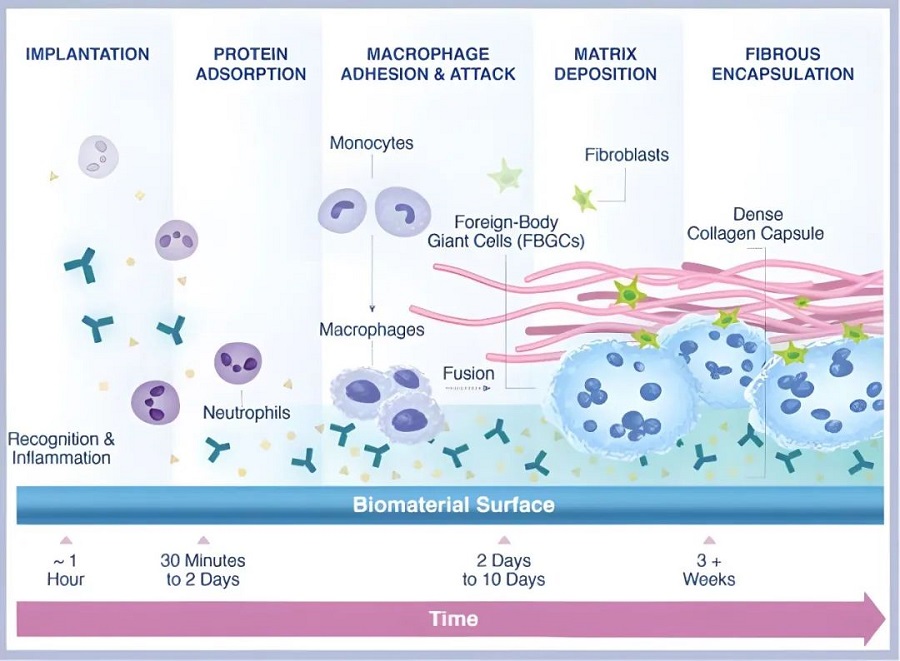
However, the scientific community has long been hindered by the limitations of traditional flow cytometry. Standard methods often require complex anti-coagulation pre-treatment, which can mask the true, immediate activation state of the cells.
Introducing Poclight's Pioneering CD Factor Detection System—a proprietary methodology designed to move beyond "static counting" and into the era of "functional insight."

Three Core Breakthroughs for Clinical Excellence
1. Resilience Against Platelet Interference In many clinical scenarios, especially with patients suffering from low platelet counts, traditional detection is prone to error due to platelet aggregation and concentration fluctuations. Poclight's unique methodology is independent of platelet aggregation and concentration, finally solving the long-standing challenge of functional assessment in low-count patients. We provide a clear, accurate diagnostic window where others see only noise.
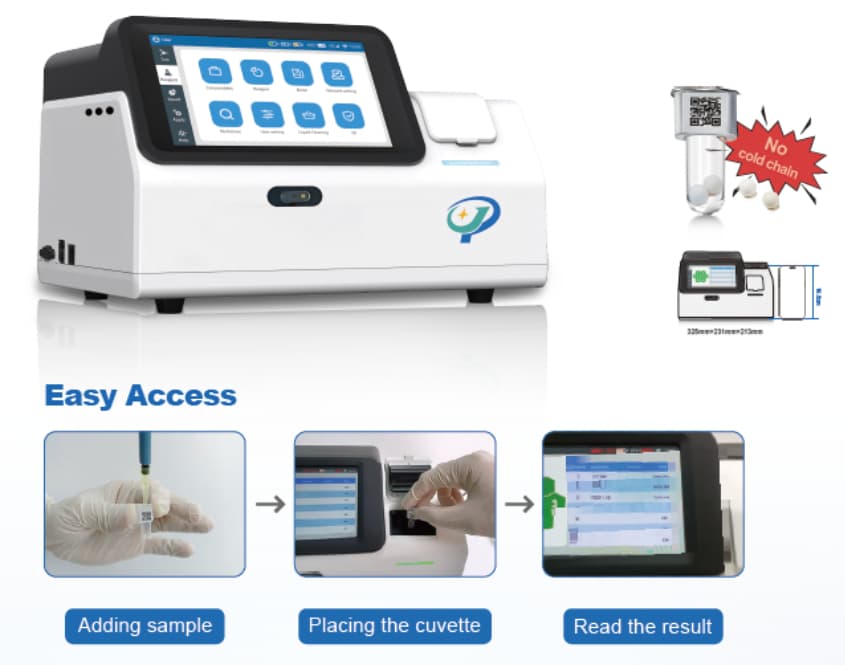
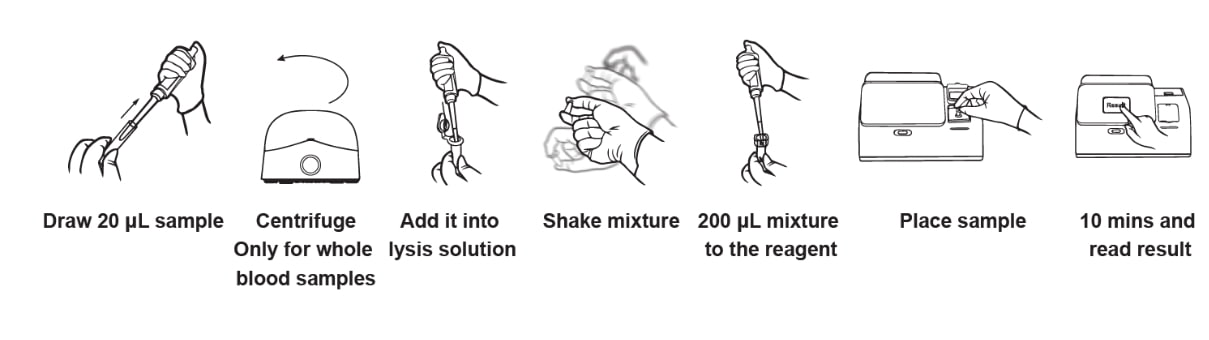
2. Standardized, High-Speed Performance Time is critical in clinical settings. Unlike the multi-step, complex pre-processing required for flow cytometry, our standardized system requires no complex pre-treatment.
Speed: Obtain reliable results in just 5–10 minutes.
Dual Functionality: Simultaneously detect platelet activation states and aggregation functions, providing a comprehensive metabolic profile of the regenerative matrix in real-time.
3. A One-Stop Solution for Life Sciences and Clinics We provide a seamless bridge between laboratory research and clinical application. By offering a one-stop solution for CD factor analysis, we are pushing the boundaries of platelet function research into a more precise, efficient, and data-driven new stage.
True Accuracy Reflects True Activation
Poclight's technology captures the authentic and immediate state of cellular activation. By reflecting the cells as they truly behave within the patient’s own biological environment, we provide clinicians with the most accurate basis for judgment.
Contact us today to discover how our exclusive CD Factor Detection Kits can redefine your outcomes.