Exudative Retinal Detachment (ERD) is a lesion in which the neuroepithelial layer of the retina separates from the pigment epithelial layer without holes. The core mechanism is the destruction of the blood-retinal barrier or the imbalance of choroidal osmotic pressure, resulting in abnormal accumulation of plasma, lipids or blood in the subretinal space. Unlike rhegmatogenous or tractional detachment, ERD does not have retinal holes. ERD is often an "ocular crisis signal" of systemic or local diseases.
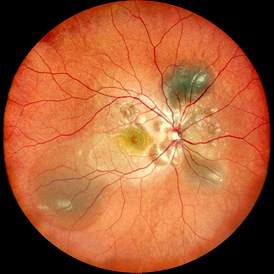
Common causes:
ERD is essentially the fundus manifestation of multi-system diseases, and its causes can be divided into two major categories:
(1) Systemic diseases and pregnancy-related diseases: Severe preeclampsia (S-PE) and HELLP syndrome are high-risk factors for ERD; Hypertensive nephropathy: Malignant hypertension can cause choroidal circulation disorders, and fibrinoid necrosis of choroidal arteriole leads to a large amount of plasma exudation. (2) Ocular diseases such as uveitis and retinal vasculitis: Uveitis ranks first among the causes of ERD, especially posterior uveitis like VOGT-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome (VKH) and sympathetic ophthalmia. Inflammation leads to increased permeability of choroidal vessels, causing exudation. Tuberculous uveitis can form subretinal abscesses or granulomas, directly damaging the blood-retinal barrier. Vascular diseases: Coats' disease - Highly prevalent in children and adolescents. Retinal capillary dilation accompanied by a large amount of lipid exudation can lead to total detachment. Retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) - Ischemic vein occlusion induces the release of inflammatory factors, leading to vascular leakage; Tumors and congenital abnormalities: Choroidal melanoma or hemangioma disrupts the blood-retinal barrier, leading to the accumulation of exudate. Metastatic breast cancer and lung cancer are the most common primary foci. According to the latest study of EURETINA 2024, exudative detachment is the main manifestation of invasive retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), accompanied by edema in the anvascular area and subretinal exudation.
Clinical manifestations:
The symptoms of ERD patients are diverse, but there are usually four key warning signs:
Painless vision loss: When the macular area is involved, vision can drop sharply to below 0.1. Unlike rhegmatogenous detachment, vision loss in ERD usually progresses more slowly, but patients in the acute phase of hypertensive crisis or VKH syndrome may lose central vision within a few hours. Visual distortion: Due to the displacement of photoreceptor cells caused by subretinal fluid, wavy distortion occurs when looking at straight lines. Amsler grid examination reveals typical grid distortion. Central dark spot: When the macular area is affected, a fixed black shadow appears in the center of the visual field, but the peripheral visual field remains relatively intact. Abnormal color vision and flashes: Inflammatory ERD (such as VOGT-Koyanagi-Harada disease) is prone to blue-yellow color vision shift.
Diagnostic method:
Multimodal imaging combined application of optical coherence tomography (OCT) : The gold standard for ERD diagnosis, which can directly display low-reflection dark areas of subretinal fluid and RPE detachment. EDI-OCT technology - enhanced penetration depth, can quantify choroidal thickness, and help distinguish VKH from CSC; Fluorescein angiography (FFA) : Active leakage foci show "ink-stained" or "chimney-like" hyperfluorescence (such as CNV); The bleeding area shows fluorescence occlusion, and the non-perfusion area suggests ischemic etiology. Indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) : Evaluation of choroidal vessels - Diagnosis of polypoid choroidal vasculopathy (PCV) or VKH complex; OCT angiography (OCTA) : Non-invasive detection of retinal/choroidal neovascularization and quantification of blood flow density; B-type ultrasound: When the refractive media is turbid, it shows subretinal fluid dark areas, differentiating choroidal tumors or hemorrhage. Multifocal electroretinography (mfERG) : Objectively assess retinal functional impairment, especially suitable for children or uncooperative patients;
Treatment and prognosis:
The treatment of ERD should focus on etiological therapy, supplemented by surgical intervention.
Drug therapy: Glucocorticoids - systemic or topical application (such as intrauterine injection) to suppress inflammation (such as uveitis, Eales' disease); Anti-vegf drugs - reduce vascular leakage (such as BRVO, Coats' disease); Laser and photocoagulation therapy: Retinal laser photocoagulation - sealing abnormal blood vessels (Coats' disease, ischemic BRVO); Micro-pulse laser - Treating macular edema and reducing thermal damage; Surgical intervention: It is only used for complex cases, such as vitrectomy when Coats' disease is secondary to traction detachment. Spontaneous absorption is possible. After blood pressure is controlled in hypertensive choroidal lesions, the detachment can spontaneously return to its original position. The prognosis is highly dependent on the control of the primary disease: inflammatory ERD - early hormone therapy can completely reset it, and the visual recovery is relatively good; Tumors or Coats' disease - Delayed diagnosis and treatment can cause permanent photoreceptor damage. Amblyopia should be vigilant in children. Follow-up requirements - OCT and FFA should be reexamined every 3 to 6 months to monitor recurrence.
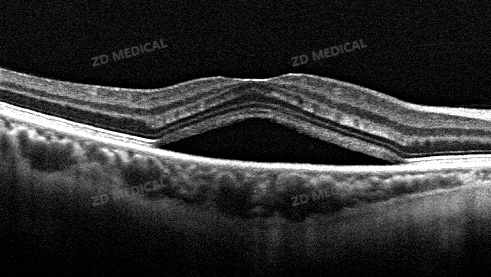
Example 1: The retinal neuroepithelial layer in the macular area protrudes, with dark reflex cavities inside
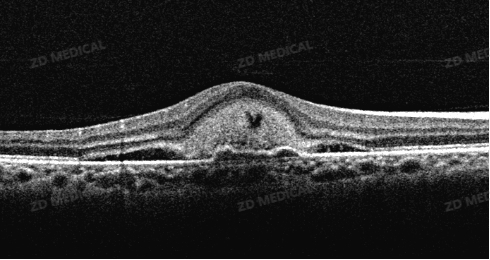
Example 2: A mass of hyperreflectivity can be seen in the central area, accompanied by subretinal effusion and shallow detachment of the retinal pigment epithelium layer
Exudative retinal detachment is a "crisis signal" of systemic diseases within the eye, and its diagnosis and treatment require collaboration between ophthalmology and multiple disciplines. Early identification of the primary disease, combined multimodal imaging assessment, and targeted control of inflammation/vascular leakage are the core strategies to avoid permanent vision loss. Especially for premature infants and patients with chronic inflammation, regular fundus screening is a key line of defense for saving visual function!
Also welcome to contact us, we are ZD Medical Inc.
Tel : +86-187 9586 9515
Email : sales@zd-med.com
Whatsapp/Mobile : +86-187 9586 9515





